IN THIS ARTICLE
ROS 2 Vehicle Dynamics
Vehicle Model
VehicleModelComponent serves the purpose of converting inputs such as target velocity, steering or acceleration to physical forces on parts of a vehicle (robot). VehicleModel has a VehicleConfiguration which is used to define axles, parametrize and assign wheels. The model requires a WheelControllerComponent present in each wheel entity. It also uses an implementation of DriveModel, which converts vehicle inputs to forces acting on steering elements and wheels.
Note:The functionality is available in theROS2ControllersGem.
Wheel Controller
A wheel controller is a controller that should be attached to the vehicle’s wheel. The wheel entity should have PhysX Hinge Joint attached. The Joint controller should have:
- Motor Configuration / Use Motor enabled,
- Motor Configuration / Force Limit Value set to a desirable value.
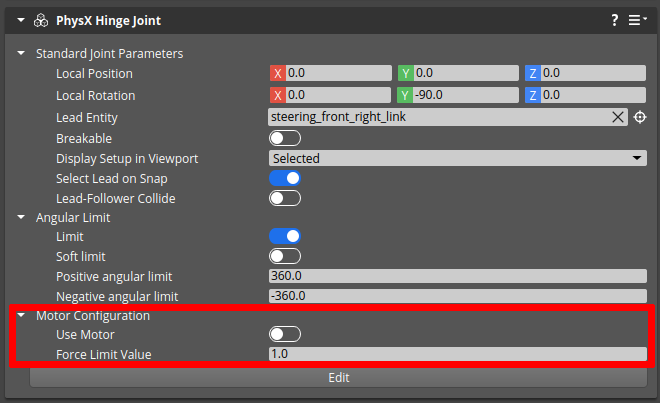
The wheel controller has the following parameters shown below.
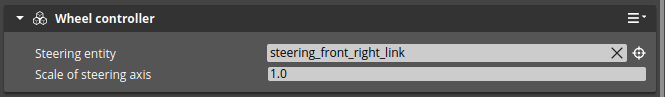
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Steering Entity | The entity that has a PhysX Hinge Joint that changes the direction of the wheel. |
| Scale of steering axis | Allows the user to change the ratio or / and direction of wheel steering. |
Ackermann Drive Model
The implementation of AckermannDriveModel uses PID controllers . The model computes velocities or forces in the joints of the vehicle and applies it accordingly to commanded velocity.
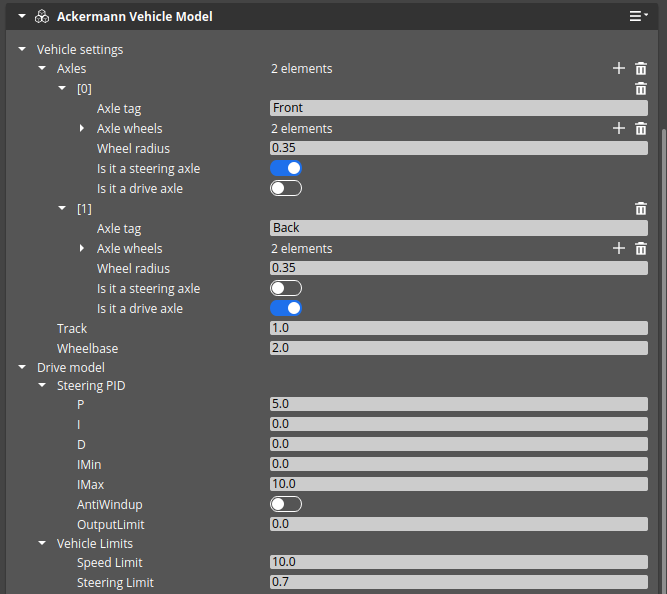
Parameters of the model are exposed to the user via AckermannVehicleModelComponent:
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DriveModel / Axles | List of axles of the vehicle. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Axle Wheels | List of wheels in axis. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Is it a steering | If it is enabled the Ackermann Drive Model will apply a steering angle. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Is it a drive | If it is enabled the Ackermann Drive Model will apply drive force. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Track | Distance between front and rear axis. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Wheelbase | Distance between left and right wheel. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / P | Proportional gain of PID controller for steering servo. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / I | Integral gain of PID controller for steering servo. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / D | Derivative gain of PID controller for steering servo. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / IMin | Minimum integration impact of PID. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / IMax | Maximum integration impact of PID. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / AntiWindUp | Prevents integral wind-up in PID. |
| DriveModel / Steering PID / OutputLimit | Clamps output to maximum value. |
| DriveModel / Vehicles Limits / Speed limit | Maximum achievable linear speed in meters per second. |
| DriveModel / Vehicles Limits / Steering limit | Maximum achievable steering angle. |
Skid Steering Drive Model
The model computes velocities in the joints of the vehicle and applies it accordingly to commanded velocity and configuration.
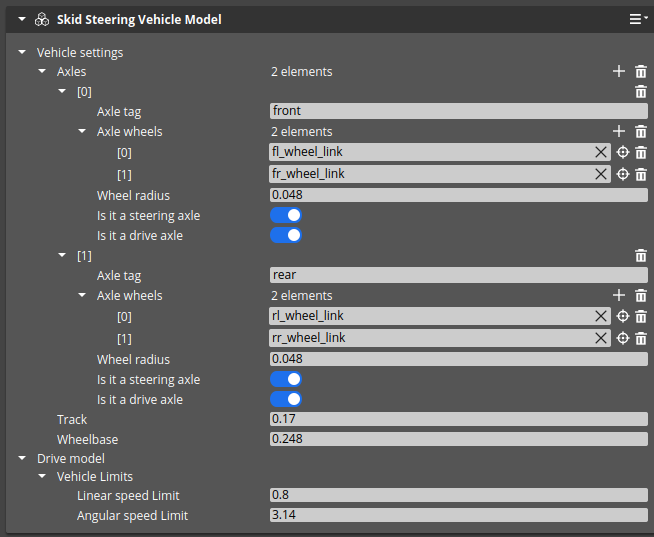
Parameters of the model are exposed to the user via AckermannVehicleModelComponent:
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| DriveModel / Axles | List of axles of the vehicle. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Axle Wheels | List of wheels in axis. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Is it a steering | It is ignored in this model. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Is it a drive | If it is enabled, the Skid Steering Drive Model will apply velocities to the axis’ wheels. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Track | Distance between front and rear axis. |
| DriveModel / Axles / Wheelbase | Distance between left and right wheel. |
| DriveModel / Vehicles Limits / Linear speed limit | Maximum achievable linear speed in meters per second. |
| DriveModel / Vehicles Limits / Angular speed limit | Maximum achievable angular speed in radians per second. |
Manual control
The VehicleModel will handle input events with names “steering” and “accelerate”. This means you can add an InputComponent to the same entity and define an input map for your input devices (such as a keyboard or a gamepad) to control the vehicle manually.
You can use tools such as rqt_robot_steering to move your robot with Twist messages. RobotControl is suitable to use with ROS 2 navigation stack .
It is possible to implement your own control mechanisms with this component.
